篇名
認識房室傳導阻滯
說明
觀念剖析
房室傳導阻滯是指神經衝動在房室傳導過程中受到阻礙的一種現象。可由心電圖來判別出一型二型三型AVB。
前言
房室傳導阻滯(atrioventricular block,AVB)是指神經衝動在房室傳導過程中受到阻礙( the impairment of the impulse conduction between the atria and ventricles of the heart)。一般可以分為不完全性房室傳導阻滯和完全性房室傳導阻滯兩類。不完全性房室傳導阻滯包括First degree AVB和 Second degree AVB;Second degree AVB聽診心律整齊與否,取決於房室傳導比例。Third degree AVB又稱完全性房室傳導阻滯,阻滯部位可在心房、房室結,喜氏束及左右束支。
病因
- 以心肌炎最常見。
- 迷走神經興奮↑(increased vagal tone)。
- 藥物,如digoxin或β-blockers、Ca+2blockers、Amiodarone。
- 各種器質性心臟病(心肌缺氧、壞死ischemic heart disease in 40%)或瓣膜病變(valvulopathy)等。
- K+、Ca2+、Mg+2等電解質不平衡。
- 傳導系統纖維化等(idiopathic fibrosis and sclerosis of the conduction system about 50% of patients)。
- 外傷,心臟外科手術時誤傷。
症狀
- First degree AVB:患者一般無症狀。聽診可發現心尖部S1減弱,此是由於P-R interval延長,心室收縮開始時房室瓣接近close所致。
- Second degree AVB:因部分心房激動不能傳至心室,一些P波後沒有QRS波群。Mobitz Type 1患者可有心搏暫停感覺;Mobitz Type 2患者常疲乏、頭昏、心臟功能不全,容易在短時間內發展為Third degree AVB。
- Third degreeAVB患者症狀取決於心室率及是否建立了心室自主節律。如心室自主節律未及時建立則出現心臟停搏(Cardiac arrest)。自主節律點在His bundle下方,心室率40~60beat/min,可能出現疲乏(Fatigue)、低血壓、頭痛、暈厥(Syncope)等症狀。左右束支病變者,心室率在40beats/min以下,可出現Heart failure和Adams-Stokes Syndrome。
(Signs include those of AV dissociation, such as cannon a waves, BP fluctuations, and changes in loudness of the 1st heart sound (S1). Risk of asystole-related syncope and sudden death is greater if low escape rhythms are present.)
EKG 檢查
一、First degree AVB:
- P-R interval>0.20秒(PR interval greater than 0.20sec)
- 每個P wave後均有QRS complex,規則的P-R interval。
(All normal P waves are followed by QRS complexes, but the PR interval is longer than normal)
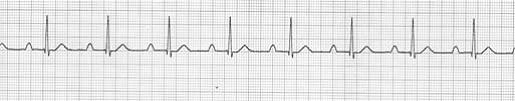
二、Second degree AVB:
部分心房激動不能傳至心室,一些P波後沒有QRS波群,房室傳導比例可能是2:1;3:2;4:3……。Second degree AVB可分為兩型:
- Second degree AVB,Mobitz TypeⅠ(aka Mobitz 1,Wenckebach):
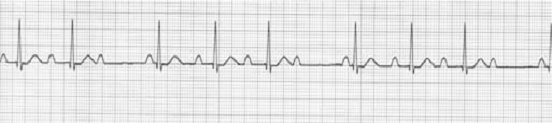
(1) P-R interval逐漸延長,而R-P interval則逐漸縮短,直到QRS complex loss,出現長R-R間歇。{the PR interval progressively lengthens with each beat until the atrial impulse is not conducted and the QRS complex is dropped (Wenckebach phenomenon); AV nodal conduction resumes with the next beat, and the sequence is repeated} 。
(2) 規則固定的P-P interval
(3) 長R-R間歇後的R-R interval>R-R interval。
(4) 長R-R間歇< 任何短R-R間歇的2倍。 - Second degree AVB,TypeⅡ(aka Mobitz 2,Hay):
(1) 規則固定的P wave,P-R interval固定。(PR interval remains unchanged prior to the P wave which suddenly fails to conduct to the ventricles)
(2) QRS complex 會突然loss,阻滯程度可為1:1、2:1、3:1、3:2、4:3等。(the PR interval remains constant. Beats are intermittently nonconducted and QRS complexes dropped, usually in a repeating cycle of every 3rd (3:1 block) or 4th (4:1 block) P wave )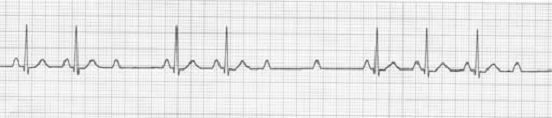
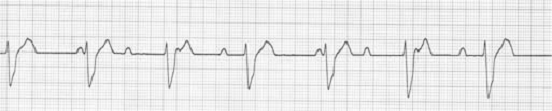
三、Third degree AVB
- 心房及心室的激動各自規律(即固定P wave 與寬大規則QRS complex)出現,P wave與QRS complex相互無關(Third degree AV block : No association between P waves and QRS complexes)。無規律的P-R interval關係。
- 心房速率比心室速率快(即P wave 的數目比QRS complex 數目多);
- QRS波群的形態主要取決於阻滯的部位;若阻滯位於His bundle以上,則心室 律可由交界區或心室起搏點來控制,這時QRS complex是不增寬的,心率40~60beats/min;但若阻滯位於左右束支,心室律由心室內低位激動點來控制,則QRS complex寬大,心率30~50beats/min。(Escape rhythms originating above the bifurcation of the His bundle produce narrow QRS complexes, relatively rapid (> 40 beats/min);Escape rhythms originating below the bifurcation produce wider QRS complexes, slower and unreliable heart rates, and more severe symptoms (eg, presyncope, syncope, heart failure))
治療
- 病因治療:First degree AVB和 Second degree AVB typeⅠ型,無poor perfusion症狀者則不需特殊處理。
- 急性感染:予以 Antibiotics 治療;
- 非特異性炎症:予以 Epinephrine ;
- 降低 Vagus nerve 興奮性:予以 atropin ;
- 停止導致 AVB 的藥物;
- 低鉀血症: KCl 靜脈滴注。
- Ⅱ度Ⅱ型AVB患者,EKG顯示QRS complex增寬畸形,臨床症狀明顯,宜安置經皮心律調整器( Trans cutaneous Pacemaker,TCP),不宜用Atropin。
- 完全性房室傳導阻滯,心室率在40次/min以上,無症狀者,可不必治療,如有Bradycardia,可吸氧,給Atropin 0.5mg/Q3~5min(Max. 3mg)、Epinephrine 2~10ug/min(可增加HR與Bp,對於心肌缺氧患者使用時要特別小心),並安置經皮心律調整器(TCP)。
關鍵詞
房室傳導、神經衝動、傳導阻滯、房室結、心肌炎、心肌缺氧
上一篇
下一篇