法洛四聯症(Tetralogy of Fallot,TOF)是一種最常見的發紺型先天性心臟病(TOF is a congenital heart defect which is the most common cyanotic heart defect, and the most common cause of blue baby syndrome)。法洛四聯症的發生率為0.2/1000左右,男性略多於女性,佔先天性心臟病(CHD)的10%,該病真正解剖特點是肺動脈狹窄及心室中隔缺損(Embryology studies show that it is a result of anterior malalignment of the aorticopulmonary septum, resulting in the clinical combination of a VSD, pulmonary stenosis, and an overriding aorta)。
近些年醫學界對TOF的認知越來越明確,以及手術技巧不斷進步,該病的治癒率越來越高,手術治療死亡率已經降至5%以下。(發展史)
|
1672年Niels Stensen首次描述其解剖特徵 |
|
1888年Étienne-Louis Arthur Fallot描述了此症的四種心臟畸形: |
|
1970年Van Praagh等認為TOF的本質是:胚胎時期,肺動脈圓錐遠段或右心室漏斗部發育不良(Period of embryo, funnel part maldevelopment)以及漏斗部間隔向左前移位(shifting)所導致 |
|
1975年,Lillihei等人認為該病與肺動脈幹的內翻不足(varus insufficient)、圓錐膈部向小梁(trabecula)間隔部之旋轉不完全有關 |
一般認為,法洛四聯症是環境、基因異常或者二者相互作用所導致的結果(Its cause is thought to be due to environmental or genetic factors or a combination),基因異常與第22號染色體部分缺失和先天性胸腺發育不全有關(It is associated with chromosome 22 deletions and DiGeorge syndrome)。
下面,我們從血流動力學的角度加強對該病的理解:
|
|
上述TOF其病理生理學變化是一種非限制性的VSD,因此,右心室壓力可升高到與左心室壓力相等的水準,右心室壓力不會超過體循環的壓力。然而,出現右心室肥厚,則是說明右心室收縮壓進一步增高所致的一種代償性改變(Right ventricular hypertrophy results from this combination, which causes resistance to blood flow from the right ventricle) |
|
4個情況 |
重點描述 |
|
Pulmonary Infundibular Stenosis |
右心室流出道狹窄可在漏斗部、肺動脈瓣膜部或瓣環,大多數病例漏斗部狹窄與肺動脈瓣膜狹窄合併存在。A narrowing of the right ventricular outflow tract and can occur at the pulmonary valve (valvular stenosis) or just below the pulmonary valve (infundibular stenosis). Infundibular pulmonic stenosis is mostly caused by overgrowth of the heart muscle wall (hypertrophy of the septoparietal trabeculae),leading to the formation of the overriding aorta. The pulmonic stenosis is the major cause of the malformations, with the other associated malformations acting as compensatory mechanisms to the pulmonic stenosis.The degree of stenosis is the primary determinant of symptoms and severity. |
|
Overriding aorta |
主動脈根部較正常增大,位於肺動脈根部的右側,主動脈向前、向右移位,位於左右心室之上。跨位在右心室的主動脈口徑變異很大;如果右心室流出道瀰漫性發育不良、漏斗部間隔狹窄、肺動脈開口向左移位者,其主動脈右位及跨位更為明顯(An aortic valve with biventricular connection, that is, it is situated above the VSD and connected to both the right and the left ventricle. The degree to which the aorta is attached to the right ventricle is referred to as its degree of "override" .The aortic root can be displaced toward the front or directly above the septal defect, but it is always abnormally located to the right of the root of the pulmonary artery. The degree of override is quite variable) |
|
ventricular septal defect (VSD) |
此乃圓錐部間隔與漏斗部間隔未能在同一平面對攏所造成(A hole between the two bottom ventricles of the heart. The defect is centered around the most superior aspect of the the outlet septum, and in the majority of cases is single and large) |
|
Right ventricular hypertrophy |
由於右心室肥厚致心尖向上翹起所致。在chest X-ray上心影呈靴形 (The right ventricle is more muscular than normal, causing a characteristic boot-shaped (coeur-en-sabot) appearance as seen by chest X-ray) |
法洛四聯症在剖學方面的變異差別很大,尤其是右心室出口流出道阻塞的程度(right ventricular outflow tract obstruction)是決定了患兒出現症狀與疾病進程的關鍵(There is anatomic variation between the hearts of individuals with tetralogy of Fallot. Primarily, the degree of right ventricular outflow tract obstruction varies between patients and generally determines clinical symptoms and disease progression)。
(臨床表現)
|
症狀 |
|
|
體徵 |
|
|
輔助 |
|
診斷
綜上所述,該病的診斷就呼之欲出了,凡具有以下特點,則可以考慮為TOF:
- 出生後數月出現紫粓伴有缺氧表現,長大過程出現採取半蹲坐姿勢之蹲踞現象;
- 理學檢查:心前區收縮期雜音伴有P2減弱;
- EKG:提示電軸右偏和右心室肥厚;
- Chest X-ray:提示肺動脈段凹陷、心影不大,心尖抬高呈靴狀;超音波、MRI、心導管、心血管造影可以確診(The abnormal "coeur-en-sabot" (boot-like) appearance of a heart with tetralogy of Fallot is easily visible via chest x-ray, and before more sophisticated techniques (echocardiography) became available, this was the definitive method of diagnosis)。
(併發症)
最常見的併發症為腦血栓、腦膿腫及亞急性細菌性心內膜炎。
(治療)
|
內科 |
1、一般治療:鼓勵飲水,防治dehydration和infection,預防complication; |
|
2、突發性發紺加重的治療: |
|
|
外科 |
治療的目的是儘快增加肺部血流,以免因缺氧造成不可逆的後遺症;
|
(問題來了)以下試題摘自考選部醫師專技考試題目
1.一位1 歲男孩,出生後即被發現有心雜音及哭鬧後嘴唇有發紺(cyanosis)現象。除嘴唇及四肢末端有發紺現象外,於左胸前可聽到第2-3 度收縮期心雜音。其胸部X 光檢查如下圖所示。下列何者為最可能之診斷?<96-1-5>
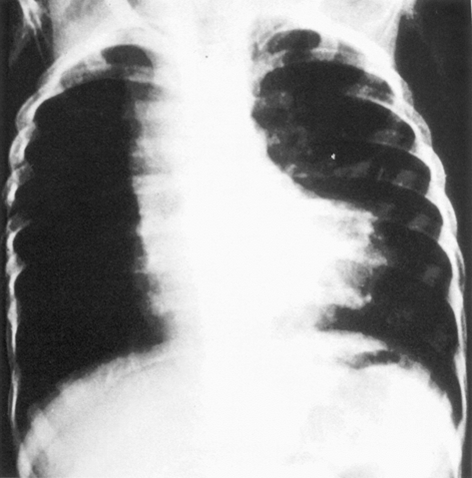
- 大血管轉位(transposition of great arteries)
- 法洛氏四合症(tetralogy of Fallot)
- 總肺靜脈回流異常(total anomalous pulmonary venous return)
- 殘存動脈幹(persistent truncus arteriosus)
2.法洛氏四合症(tetralogy of Fallot)之心雜音是何種畸形造成? < 97-1-34 >
- 肺動脈下漏斗體狹窄(infundibular stenosis)
- 心室中隔缺損(ventricular septal defect)
- 右心室肥厚(hypertrophic right ventricle)
- 主動脈跨位(overriding of aorta)
3.16 個月男嬰,因排便後突然發生呼吸急促,發紺加劇而送至急診。此孩童以往即被發現有發紺及心雜音,其胸部X 光片顯示肺血管減少,心臟形狀似“馬靴”(boot- shaped)。下列何種處理較不適當? < 97-2-29 >
- 馬上將孩童置膝抱胸(knee-chest)姿勢,並給予氧氣
- 給予碳酸氫鈉(NaHCO3)以矯正酸血症
- 避免孩童躁動而更消耗氧氣,給予benzodiazepam 鎮靜
- 給予靜脈注射propranolol,減緩肺動脈下漏斗體(infundibulum)之收縮
4.5 天大男嬰,被發現有呼吸窘迫、發紺、及心雜音。呼吸次數每分鐘74 次合併厲害胸凹現象,肝臟於右肋骨下5 公分摸得到,其右手血壓為66/40 mmHg,左手及下肢血壓約為44/20 mmHg。同時合併低血鈣。下列何者為不適當的處理? < 98-1-7 >
- 給予氣管插管(intubation)維持呼吸,並給予氧氣
- 給予靜脈注射dopamine、dobutamine
- 給予靜脈注射indomethacin
- 抽血檢查是否合併染色體22 q11 缺失症
5.一位1歲男孩,於早晨排便後,被發現呼吸急促及發紺加劇現象而送到急診。其胸部X光檢查如圖所示。據家屬描述,該男孩出生後即被發現有心雜音及哭鬧後嘴唇有發紺(cyanosis)現象。下列何者為不適當處置?< 99-1-29 >
- 避免孩童哭鬧持久消耗更多氧氣,給予diazepam
- 給予氧氣,並將孩童置膝抱胸(knee-chest)姿勢
- 給予靜脈注射propranolol藥物
- 給予靜脈注射sodium bicarbonate矯正代謝性酸血症(metabolic acidosis)