篇名
認識WPW現象
說明
觀念剖析
WPW是一種異常房室傳導現象,衝動經accessory pathway下傳,提早興奮心室,引起部分心室肌提前激動現象,常伴有PSVT時,會引起面色蒼白、心悸、頭暈、氣短、胸痛,甚至暈倒等症狀。WPW syndrome的典型EKG表現是P-R interval縮短及寬的QRS complex中出現Delta wave。
前言
預激(pre-excitation)是一種異常房室傳導現象,衝動經accessory pathway下傳,提早興奮心室,引起部分心室肌提前激動現象,稱為預激症候群(pre-excitation syndrome)或WPW(Wolf-Parkinson-White syndrome),常合併PSVT、Af,甚至Vf發作。診斷主要依據EKG。WPW有時與一種粒線體病變所導致的眼神經疾病有關。(WPW is a syndrome of pre-excitation of ventricles of the heart due to an accessory pathway. This accessory pathway is an abnormal electrical communication from the atria to the ventricles. WPW is a type of atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia)( WPW syndrome is sometimes associated with Lebers hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON), a form of mitochondrial disease)。
病理生理
正常情況下,心房與心室之間神經傳導必須經過AV node這個“關口守門員(gatekeeper)”,並且有0.1秒左右的不反應期(Refractory period)。然而,當胚胎時出現發育異常,在心房與心室之間產生accessory pathway而自成一條神經傳導路徑。由於這條異常的accessory pathway並沒有延遲現象,因此,造成心臟過早激化,最常見accessory pathway是Kent bundle,神經傳導可以是anterograde或retrograde。(WPW is a syndrome of pre-excitation of ventricles of the heart due to an accessory pathway known as the bundle of Kent. bundle of Kent is an abnormal electrical communication from the atria to the ventricles. This accessory pathway does not share the rate-slowing properties of the AV node, and may conduct electrical activity at a significantly higher rate than the AV node)。
假設一個人心房速率是300 beats/min,由於accessory parhway無延遲現象,所以引起心室速率也是300 beats/min,如此快速的心室率是非常危險的,不但可引起血流動力學的異常,容易出現Vf心律不整而造成猝死。
(an individual had an atrial rate of 300 beats per minute, the accessory bundle may conduct all the electrical impulses from the atria to the ventricles, causing the ventricles to activate at 300 beats per minute. Extremely fast heart rates are potentially dangerous, and cause hemodynamic instability. In some cases, the combination of an accessory pathway and cardiac arrhythmias can trigger Vf, a leading cause of sudden cardiac death)。
發生率
約有千分之一~三的人群有WPW syndrome,任何年紀都可能發生WPW syndrome的心動過速,但隨著年紀增加,accessory pathway的神經傳導速度會減慢,因此在EkG上會表現preexcitation的cases會減少。但已經在EKG上有WPW syndrome型態者,隨者年齡的增長,PSVT的機會也會隨之增加,根據統計,WPW 伴有Af,由於常有很的傳導性衝動從accessory pathway下傳到心室,所以在EKG會有”bizarre, wide-complex, irregular”之心率過速,心率會達到250 beats/min以上。WPW with Af約11~38%的發生率,因容易變成Vf,是WPW中最易致死的心律不整。在20~39歲WPW syndrome伴有PSVT者占10%左右,而超過60歲發生率可達35%。
臨床表現
患者一般是無症狀的,然而常伴有PSVT時,常會引起面色蒼白、心悸、頭暈、氣短、胸悶,偶有暈倒等症狀(Patients are usually asymptomatic. However, during supraventricular tachycardia the individual may have symptoms of palpitations (sudden onset and termination of a fast heart rate), dizziness, shortness of breath, and occasionally fainting/near fainting during episodes of supraventricular tachycardia)。
EKG檢查
WPW syndrome的典型EKG表現是縮短的P-R interval,有Delta wave 的寬QRS complex。這是因為經由 accessory pathway的傳導性衝動,會比經由典型AV node傳下來的傳導性衝動提早到達心室,產生了所謂preexcitation,形成了所謂的Delta wave, 而使得QRS interval變寬,P-R interval變短。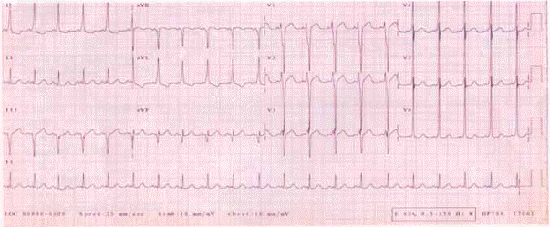
分型
關於Bundle of Kent:若是左心房與左心室之間的Bundle of Kent所引起的預激,依據Delta wave/QRS complex在precordial leads的形狀,則為Type A型預激;若是右心房與右心室之間的Bundle of Kent所引起的預激,則為Type B型預激。ECG 的圖形表現是依據二者傳導性衝動的相對速度的不同而定,當accessory pathway的傳導性衝動下傳速度快過AV node的不反應期時,在ECG上就會被發現,這種叫作latent accessory pathway,可以有順向(antegrade)與逆向(retrograde)的傳導;若經由accessory pathway與AV node的傳導性衝動同時到達心室, 此時在ECG上是看不出有preexcitation。
(1) type A 型:是在 V1~V6 lead 的 Delta wave 都是 upright positive ;因為 accessory pathway 的傳導性衝動是由 LA 後壁進入 LV 後壁,因此在 lead V1 的 R 會比 S 大;
(2) type B 型:的 Delta wave 是負向的,因此,在 V1 和 V2 lead 會有 negative 的 Delta wave 和 QRS complex,這是因為 accessory pathway 的衝動,由 RA 後面或側面進入 RV,所以 V3-V6 的 Delta wave/QRS complex 都是 upright positive,但 V1~V2 是 negative。
(In case of type A pre-excitation (left atrioventricular connection), a positive R wave will be seen in V1 (positive delta) on the precordial leads of the ECG , while in type B pre-excitation (right atrioventricular connection), a predominantly negative delta wave will be seen in lead V1 (negative delta)
WPW with Af 時,因常常有許多的衝動從 accessory pathway 下傳至心室,因此在 ECG 會有 bizarre, wide-complex, irregular 之 tachycardia,心率可達到 250 beats/min 以上。
治療
- ECG只是顯示有pre-excitation,從來沒有過心率過速,一般是不須進一步電生理檢查 (cardiac electrophysiologic studies,EP)或治療。
- 2WPW有三個主要治療方式,即藥物治療、electrical ablation、和surgical ablation:
- 對於有症狀的WPW syndrome:Ablation是第一線的治療方式。根據既往的統計WPW患者予以radiofrequency catheter ablation治療的成功率高達95%。
(success rates of as high as 95% in patients treated with radiofrequency catheter ablation for WPW) - 藥物治療:拒絕ablation之患者,或ablation卻失敗1~2次以上者。可使用membrane-active antiarrhythmic drug (class IC,如amiodarone, sotalol or III)+AV nodal blocker(Ca+2 blockers、β-blockers、digoxin),或procainamide+verapamil (class IA+ IV)、quinidine+propranolol (class IA+ II)。單獨使用AV nodal blocker會誘發Af。
- 對於有症狀的WPW syndrome:Ablation是第一線的治療方式。根據既往的統計WPW患者予以radiofrequency catheter ablation治療的成功率高達95%。
- WPW伴有atrial fibrillation(Af)
(1) 治療原則:- 拉長accessory pathway 的不反應期,使accessory pathway的不反應期比AV node的不反應期更長;
- 讓accessory pathway向前傳導的傳導性衝動減慢,從而使心室搏動也減慢;
【註】一般經由AV node的Af是讓AV node的不反應期拉長,這跟WPW產生Af 不同。 - 若無血液動力學異常,身體處在stable狀態時,可嘗試使用procainamide(iv)+β-blocker或cardioversion的處理,單獨使用procainamide可控制經由accessory pathway產生的Af,但有可能產生經由AV node來傳導的Af
- 若有血液動力學異常,出現hypotensive、 hypoperfusion症狀者,首選synchronized cardioversion。
(Adenosine and other AV node blockers should be avoided in atrial fibrillation with WPW; this includes adenosine, diltiazem, verapamil, other calcium channel blockers and beta blockers.Beta-blockers and other pharmacological agents that slow the conduction through the AV pathway (such as digoxin) should be avoided, because they will exacerbate the syndrome, by blocking the normal hearts electrical pathway, therefore exaggerating the pre-excitation pathway (Bundle of Kent))。
關鍵詞
WPW現象、異常房室傳導現象、心動過速、預激症候群、心室肌提前激動、發育異常、神經傳導、心律不整、藥物治療、臨床醫學資訊館
上一篇
下一篇