篇名
認識Prader-Willi症候群
說明
觀念剖析
染色體疾病(chromosomal disorder)種類非常多,但是新生兒常染色體(autosomal inheritance)疾病有共同特徵:即手、面部畸形(face malformation)和明顯肌張力低下(muscle hypotone)。因此,對於有肌張力低下的新生兒,伴有面部、手部畸形,都必須做染色體檢查。本次我們主要討論的是“普拉得威利症候群”(Prader-Willi syndrome,PWS)。Prader-Willi syndrome,又稱為Prader-Labhar-Willi syndrome,是罕見的一種染色體遺傳疾病(rare genetic disorder),臨床特徵是低下的肌張力、性腺功能減退(hypogonadism)、輕~中度智慧障礙(mental retardation)、身材矮小(short stature)、肥胖(obesity)等。發病率1/10000~1/25000。
目前已知發病肇因於第15號染色體上的一段編碼小核內核糖核蛋白(SNRPN)基因缺陷所致,這個片段上的基因以一種印跡(Imprinting)的遺傳機轉被調控著,因此:
|
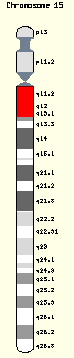 |
臨床表現
各時期的臨床表現有許多特徵,包括:
- 出生時:通常臀位或剖腹產生出(Often breech or caesarean births)、昏睡(Lethargy)、肌張力低下(Hypotonia),由於肌肉張力欠佳影響吸吮反射,導致餵養困難(Feeding difficulties due to poor muscle tone affecting sucking reflex)。
- 嬰幼兒期:生長遲滯(Failure to thrive,continued feeding difficulties)、智能延遲(intellectual delay)、嗜睡(Excessive sleeping)、斜視(Strabismus)、脊椎側灣(Scoliosis) 。
- 童年期:語言發展延遲(Speech delay)、身體協調性差(Poor physical coordination)、貪吃與食慾變佳(Hyperphagia),血中高葛洛林水準(high ghrelin levels)、體重過重(Excessive weight gain)、睡眠障礙(Sleep disorders)、脊椎側灣(Scoliosis)。
- 青春期:青春期延遲(Delayed puberty)、身材矮小(Short stature)、肥胖(Obesity)
- 成年期:不孕(Infertility)、性腺機能減退(Hypogonadism)、陰毛稀少(Sparse pubic hair)、肥胖(Obesity)、肌張力低下Hypotonia、智慧與學習能力低下(Learning disabilities)、糖尿病傾向(Prone to DM)。
【註】 1992年Curfs和Frym兩位學者總結PWS中不同的學習障礙(learning disability)程度,結果如下: IQ >85 5% average to low average intelligence IQ 70~ 85 27% borderline intellectual functioning IQ 50~70 39% mild intellectual disability IQ 35~50 27% moderate intellectual disability IQ 20~35 1% severe intellectual disability IQ < 20 <1% profound intellectual disability
下面是Prader-Willi Syndrome診斷歸納:
| 主要診斷標準 |
|
| 次要診斷標準 |
|
| 支持性診斷證據 |
|
| 【註1】 | 主要診斷標準每項 1 分,次要標準每項 0.5 分。 |
| 【註2】 | 3歲以下得5分(其中至少4分必須是主要診斷標準)才可診斷此病;3歲以上,需得8分(其中至少5分是主要診斷項目)才可以確診。 |
輔助檢查
甲基聚合酶連鎖反應作為第一線分子診斷的工具,用以判定PWS 可靠性達100%,又以螢光原位雜交做基因缺失與否的判定,檢查15號染色體長臂微小(deletion of 15q11-13)。(1) 70%患者為父系15號染色體異常。
(2) 25%患者為15號染色體母系雙倍體,缺少父系15號染色體。
(3) 5%患者為15號染色體長臂重組。
治療
該病沒有特異性治療(no cure),控制肥胖必須注意控制飲食。對症處理:如無肥胖併發症(如糖尿病或肺通氣不良),可考慮用睾丸酮替代治療(testosterone replacement)。激素替代療法(hormone replacement therapy)可以減輕症狀(lessen the conditions symptoms),如補充生長激素,可以增加肌肉張力,減輕體重(GH supports linear growth and increased muscle mass, and may lessen food preoccupation and weight gain)。
復健治療:可以改善肌肉張力及語言能力等(Improve muscle tone and speech)
思考 你能回答嗎?
Q:臨床上,Prader-Willi 症候群及 Angelman 症候群是不一樣的疾病,但是檢驗時發現兩個不同診斷的病人卻有相同的 15 號染色體微小缺損。最有可能是什麼原因?A:Prader-Willi 症候群患者之缺損染色體是遺傳自父親;Angelman 症候群患者之缺損染色體是遺傳自母親。
關鍵詞
Prader-Willi症候群、染色體疾病、打噴嚏、普拉得威利症候群、核內核糖核蛋白、新生兒、肌張力低下、畸形、臨床醫學資訊館
上一篇
下一篇